Cubeta (celda de muestra, celdas de absorción) es básicamente un tubo de ensayo diseñado para el análisis óptico. Cubetas estándares normalmente tienen la sección transversal cuadrada o triangular para evitar defectos de refracción. Material depende una parte de la cubeta - puede ser cuarzo o vidrio óptico. Cubetas de plástico se usan también, pero para actividades menos frecuentes.
Características del producto+
Technical Information+
Vial Finish Specifications
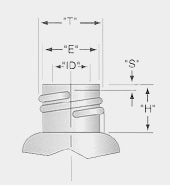

Screw Thread Finishes
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
Typical GPI finishes found in the chromatography field are as follows:
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
GPI refers to the "Glass Packaging Institute"
The GPI is responsible for establishing and issuing standards for the types and finishes produced by American glass manufacturers.
Glass Technical Information
Borosilicate - A glass that is high in silicate and having at least 5% boron oxide.
Linear Coefficient of Expansion - Fractional change in length of glass per degree change in temperature.
Strain Point - Maximum temperature to which glass should be heated during use"
Types of Glass:
USP Type - Pharmaceutical glass containers can be classified as USP Type I, II, III or NP.
Type I - Borosilicate glass represents the least reactive glass.
Type I glass has the least pH shift. (Lowest leaching characteristics) Coefficient of Expansion = 33 or 51 for Clear and 51 for Amber
Type II - is de-alkalized soda lime glass with higher levels of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide.
Type III - soda lime glass - cannot be autoclaved.
Type NP - general purpose soda-lime glass used where chemical durability and heat shock are not factors.
Coefficient of Expansion = 92.
GLASS PROPERTIES
| Color |
Clear |
Amber |
|---|---|---|
|
Linear Coefficient of Expansion |
33 |
51 |
|
Strain Point (Degrees Celsius) |
515 |
535 |
|
USP Class Type |
Type 1 |
Type 1 |
|
Light Protection |
No |
Yes |
Plastic Properties
| Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic | Type of Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
| Maximum use temperature, C/F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F | 80°C/176°F |
SEPTA SELECTION GUIDE
| Materials | Compatability | Incompatability | Resealability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone | Alcohols, acetone, ether, DMF, DMSO |
ACN, THF, chloroform, pyridine, benezene, toluene, hexane, heptane |
VERY GOOD |
| PTFE/Silicone PTFE/Silicone/PTFE |
PTFE resistance until punctured then septa or liner will have silicone compatability |
|
VERY GOOD VERY GOOD |
| Rubber (Natural Butyl)
|
ACN, Acetone, DMF, alcohols Diethylamine, DMSO, Phenol |
Chlorinated solvents, aromatics, hydrocarbons, carbon disulfide |
EXCELLENT |
| Natural PTFE/ Natural Rubber Butyl PTFE/Butyl |
PTFE resistance until punctured then septa or liner will have rubber compatability |
|
VERY GOOD VERY GOOD |
| Viton*
|
Chlorinated solvents, benezene, toluene, alcohols, hexane, heptane |
DMF, DMSO, ACN, THF, pyridine dioxane, methanol, acetone |
VERY GOOD
|
Process Flow Diagram+
The workers clean the tubing with cloth
The workers plug the tubing into machine for making vials
The vials are transferred to QC for Physical Test
The workers put the tested vials into one big package (500-800pcs/pack)
The workers get the vials from big package and put the vials into one special tray.
Put the tray with vials into the Water injection machine
The vials in tray will be transferred to next step for Ultrasonic oscillations.
The vials in tray will be transferred to Jilt water machine.
The vials in tray will be transferred to Infrared drying case.
The workers will collect the vials after vials are dry.
The vials in tray will be transferred to next step for Ultrasonic oscillations.
The workers will check all the vials inclouding the bottom neck ,bottom ,inerts.
The workers will pack 100pieces vials into one package.
The workers will send the package to sealing machine for packing.
FAQ+
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN SELECTING AN AUTOSAMPLER VIAL
Autosampler Compatibility
Not all autosamplers are alike. Some utilize robotic arms to pick up a sample vial; some use tray rotation while others move the sampling needle to the respective vial coordinates. The dimensions of autosampler vials vary. Most autosamplers are equipped with trays that use 12x32mm vial ...Not all autosamplers are alike. Some utilize robotic arms to pick up a sample vial; some use tray rotation while others move the sampling needle to the respective vial coordinates. The dimensions of autosampler vials vary. Most autosamplers are equipped with trays that use 12x32mm vial ...
MOREWHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN SELECTING AN AUTOSAMPLER VIAL
Autosampler Compatibility
Not all autosamplers are alike. Some utilize robotic arms to pick up a sample vial; some use tray rotation while others move the sampling needle to the respective vial coordinates. The dimensions of autosampler vials vary. Most autosamplers are equipped with trays that use 12x32mm vial ...Not all autosamplers are alike. Some utilize robotic arms to pick up a sample vial; some use tray rotation while others move the sampling needle to the respective vial coordinates. The dimensions of autosampler vials vary. Most autosamplers are equipped with trays that use 12x32mm vial ...
MOREInquiry
If you have any question or comment, please contact us without hesitation. We will reply you as soon as possible. ( * is required information)
¿TIENE ALGUNA PREGUNTA SOBRE NUESTROS PRODUCTOS?
CONTACTO